Introduction
In the world of emergency feedback, knowing how to check for responsiveness is a crucial skill that can indicate the distinction between life and death. Whether you're a typical bystander or a qualified health care specialist, comprehending the nuances of analyzing a casualty's condition is necessary. This write-up intends to provide extensive insights into different elements of examining responsiveness in emergency situations. By delving right into topics such as basic vs advanced life support, health center codes and procedures, and public defibrillator usage, we will equip you with the knowledge needed to act successfully when it matters most.
How to Successfully Inspect Responsiveness in Emergencies
When confronted with an unconscious or less competent person, your initial job is to establish their level of responsiveness. Yet how do you set about this? The process begins with a comprehensive assessment of the casualty's state:
Approach Safely: Make sure the location is secure for both you and the victim. Assess Responsiveness: Carefully shake the individual's shoulder and noisally ask if they're okay. Check Breathing: If there's no action, look and listen for typical breathing.This fundamental strategy establishes the stage for more advanced treatments if necessary.
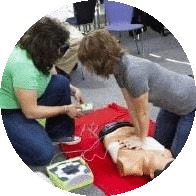
The Value of Checking Responsiveness
Checking responsiveness serves as an entrance to additional medical treatment. Understanding whether an individual is receptive help in establishing whether basic life support (BLS) or advanced life support (ALS) actions are required.
Basic vs Advanced Life Support
- Basic Life Support (BLS) covers crucial techniques such as CPR and using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED). Advanced Life Assistance (ALS) includes innovative clinical interventions normally executed by healthcare professionals.
Understanding these differences stresses why examining responsiveness is essential; it dictates which procedure should be activated.
Identifying No Breathing
One essential facet of emergency situation feedback is identifying whether someone is taking a breath or not. Identifying "no breathing" can be tough but important:
Look: Observe upper body movements. Listen: Position your ear near their mouth to listen to breath sounds. Feel: Check for air motion against your cheek.If an individual isn't breathing, launch mouth-to-mouth resuscitation quickly while asking for emergency situation help.
Maintaining Calmness Throughout Emergencies
When confronted with emergencies, it's very easy to panic, however keeping calmness can considerably enhance end results:
- Take deep breaths. Focus on what requires to be done detailed. Remind yourself that you have training or understanding that can help.
Composure permits you to believe clearly and act decisively when examining responsiveness and offering care.
Public Defibrillator Usage
Public rooms typically have Automated Outside Defibrillators (AEDs) readily available, making it crucial to know exactly how they work:
Locate neighboring AEDs: Acquaint yourself with local facilities where AEDs are placed. Follow directions on device: A lot of AED devices give audio prompts directing customers with the process. Administer shocks if necessary: Use AED after analyzing no breathing and calling emergency services.Knowing exactly how to use these tools can dramatically boost survival prices throughout heart emergencies.
Hospital Codes and Protocols
Every hospital has established procedures concerning emergency actions:
- Codes like "Code Blue" generally suggest a patient calling for prompt resuscitation efforts. Familiarizing yourself with these codes can improve communication when turning over a casualty to clinical staff at a healthcare facility setting.
Taking Activates Compressions
Performing mouth-to-mouth resuscitation efficiently calls for endurance and emphasis; hence taking turns on compressions can be helpful:
Change rescuers every 2 mins if possible. Ensure that compressions are consistent without interruption throughout handoffs. Maintain appropriate deepness-- ideally concerning 2 inches in grownups-- and rate-- at the very least 100 compressions per minute.These ideas make certain that premium compressions are preserved throughout until specialist help arrives.
Lower Compression Depth vs Higher Compression Depth
The compression depth Online CPR course Gold Coast throughout mouth-to-mouth resuscitation has significant implications:
- A lower compression deepness could not circulate blood effectively sufficient, whereas unfathomable might create injury.
The suitable deepness normally falls around 5-- 6 cm (regarding 2-- 2.5 inches) for grownups however ought to always be examined based upon situational needs.
Slow Compression Rate
While maintaining ample speed is important during CPR compressions, sluggish compression prices may lower effectiveness:
- Aim for consistent rhythmic compressions without hurrying through them.
A fast however controlled strategy makes certain maximum blood flow till emergency -responders take over care.
FAQs
1. What should I do initially when I find someone unresponsive?
First, ensure safety and security for both you and the victim prior to examining their responsiveness by carefully shaking them and asking if they are okay.
2. Just how do I understand if a person requires CPR?
If the individual does not react verbally or literally after trembling them and reveals indications of First aid training Palm Beach no breathing or uncommon breathing patterns, start CPR immediately.
3. Can any individual utilize a public defibrillator?
Yes! Public defibrillators are created for use by laypersons; several come with clear voice instructions leading customers with each action of operation.

4. What are hospital codes?
Hospital codes refer to specific expressions used within clinical facilities indicating certain emergencies necessitating instant reaction from personnel-- like "Code Blue" signaling cardiac arrest situations.
5. Is BLS certification necessary?
While it's not compulsory for everyone, acquiring BLS accreditation prepares individuals for emergency situation circumstances including adult sufferers requiring basic life support strategies effectively.
6. The length of time should I execute mouth-to-mouth resuscitation prior to stopping?
Continue executing mouth-to-mouth resuscitation up until expert assistance arrives or up until you see signs of recovery such as regular breathing or movement from the casualty.
Conclusion
Understanding how to successfully inspect responsiveness in emergency situations encompasses numerous critical aspects-- from identifying no breathing signs to using public defibrillators efficiently. The capability to preserve calmness under pressure while taking definitive actions like performing top notch CPR can not be overemphasized; they contribute dramatically toward improving survival rates in essential situations.
Equipping oneself with knowledge concerning health center codes and protocols further improves communication upon moving care to expert responders-- an important step toward guaranteeing optimum end results in dilemma situations involving subconscious individuals needing prompt help! Therefore, whether you're a day-to-day resident or component of health care training programs such as BLS qualification programs-- mastering these skills will certainly encourage you with self-confidence when it genuinely counts!